Author: Bob Brensel | President, Pharmacist | ScriptWorks
Bob Brensel, RPh, earned his Pharmacy Degree at University of the Pacific in Stockton, California in 1980. Former California Pharmacists Association’s Award Winner for Recognition of Outstanding Achievement in Compounding Pharmacy. Read More →
California is home to nearly 40 million residents, with an estimated 5–6 million women between the ages of 45 and 64 — the age range most commonly associated with perimenopause and menopause. A significant portion of these women may experience symptoms such as hot flashes, mood changes, sleep disturbances, and vaginal dryness, which can affect quality of life. For some patients, individualized hormone replacement therapy is prescribed by a licensed provider as an option to manage certain symptoms when clinically appropriate.
Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT) uses hormones that are structurally identical to those produced naturally in the body. In women’s health, BHRT is prescribed based on individual hormone levels, symptoms, medical history, and clinical goals under licensed medical guidance.
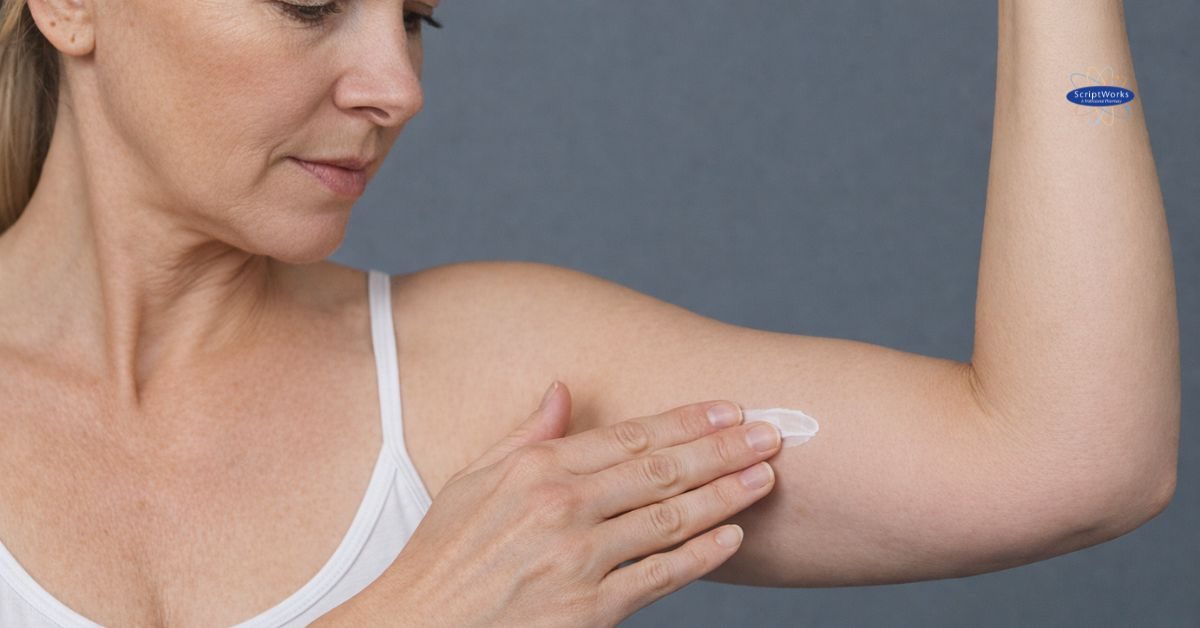
Compounded bioidentical hormones are often prepared as topical creams. When using BHRT cream, application technique matters. Where hormone cream is applied can influence how consistently medication is absorbed and how systemic exposure is maintained within an individualized care plan.
This guide explains how to apply hormone cream, where to apply BHRT cream for consistent absorption, and how compounded formulations are monitored within coordinated hormone therapy management.
Understanding Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) refers to the use of hormones that are chemically similar to those naturally produced by the body. These hormones may be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider to support women experiencing symptoms associated with hormonal changes during perimenopause or menopause.

Compounded BHRT creams are customized formulations prepared by a licensed pharmacy to align with an individual patient’s specific hormone levels, dosage needs, and delivery preferences. A prescriber may consider a topical cream over other dosage forms for patients who prefer a non-oral option, who may have difficulty swallowing tablets, or when a transdermal delivery method is clinically appropriate. Transdermal application allows the hormone to be absorbed through the skin and into the bloodstream, which may help support steady absorption over time and may be considered when a provider is evaluating factors such as gastrointestinal tolerance, metabolism, or patient-specific risk considerations.
Because each woman’s hormonal profile, medical history, and symptom presentation may vary, providers sometimes include compounded creams as part of an individualized care plan. Below is a brief overview of some of the most commonly prescribed compounded BHRT creams.
Testosterone Cream in Women’s Hormone Therapy
Women produce testosterone in small amounts via the ovaries and adrenal glands. Testosterone cream may be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider for women who have clinically evaluated low testosterone levels and are experiencing symptoms such as low libido, reduced energy, or changes in mood, when hormone support is considered appropriate as part of an individualized care plan. In some structured dosing and monitoring plans, low-dose compounded testosterone may be included.
Following transdermal absorption, testosterone binds to androgen receptors in tissues. Meanwhile, a portion may convert to estradiol through aromatase activity, which is why dosing and monitoring occur under provider oversight.
Bi-Est & Estradiol Creams
Estrogens play roles in:
- Bone physiology
- Cardiovascular function
- Genitourinary tissue integrity
- Menstrual cycle regulation
Bi-Est cream, a compounded formulation typically containing estradiol and estriol, may be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider for women experiencing symptoms associated with declining estrogen levels — such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood changes, vaginal dryness, or sleep disturbances — when hormone support is considered appropriate as part of an individualized care plan.
Bi-Est cream, a compounded formulation typically containing estradiol and estriol, may be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider for women experiencing symptoms associated with declining estrogen levels — such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood changes, vaginal dryness, or sleep disturbances — when hormone support is considered appropriate as part of an individualized care plan.
Progesterone Cream
Progesterone is often included when estrogen therapy is prescribed for women requiring endometrial protection.
Progesterone cream may be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider for women experiencing symptoms associated with progesterone decline — such as irregular menstrual cycles, sleep disturbances, mood changes, or concerns related to estrogen balance — when hormone support is considered appropriate as part of an individualized care plan.
DHEA Cream
DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) functions primarily as a precursor hormone.
After skin absorption, DHEA may convert into:
- Testosterone
- Estrogens
DHEA cream may be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider for women experiencing symptoms potentially associated with declining adrenal hormone levels — such as low energy, reduced libido, mood changes, or vaginal dryness — when hormone support is considered appropriate as part of an individualized care plan.
California Hormone Testing Kits: At-Home Collection for Maximum Convenience
Saliva testing is one method that measures certain free (biologically active) hormone levels. Hormones that may be assessed include:- Cortisol
- Estrogens
- Progesterone
- Testosterone
- DHEA
Results are interpreted alongside symptoms, medical history, blood testing when appropriate, and overall therapy goals. Saliva testing is one tool among several and is not typically used as the sole basis for clinical decisions.
How to Apply Hormone Cream
Applying hormone cream correctly helps support consistent absorption and predictable dosing. Following the same routine each day and using the recommended site helps maintain consistent absorption under medical supervision.
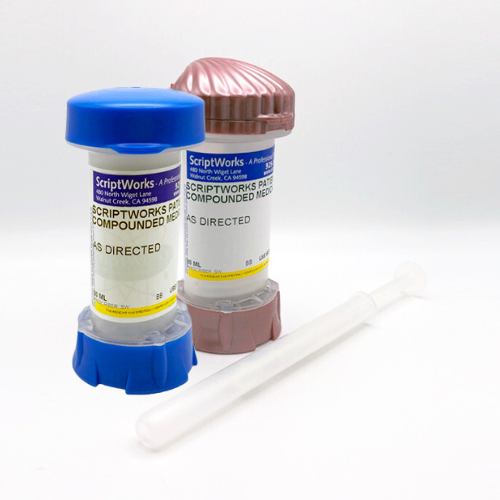
How to Use a Topi-Click Applicator
Compounded hormone creams are frequently dispensed using metered applicators like Topi-Click, which release a fixed volume per activation.
- 1 click = 0.25 mL
- 2 clicks = 0.5 mL
- 3 clicks = 0.75 mL
- 4 clicks = 1 mL
Even small variations in applied volume may influence systemic exposure. Therefore, prescribers determine both the formulation strength and how dosing will be monitored over time.
Directions:
- Remove cap.
- Ensure the applicator surface is clean.
- Activate prescribed number of clicks.
- Apply directly to the instructed site.
- Replace cap, and store as directed.
Avoid estimating doses manually.

Best Areas to Apply Hormone Cream
When asking how to apply BHRT cream or where to apply it, commonly recommended regions include:- Inner forearm
- Inner thigh
- Abdomen
- Relatively thin skin
- Adequate surface area
- Discreet coverage to reduce transfer
Where Not to Apply Hormone Cream
Avoid:
- Breasts
- Face
- Broken skin
- Mucosal areas (unless instructed)
- Areas prone to heavy friction
Common Mistakes When Applying Hormone Cream
- Applying to wet skin
- Skipping rotation entirely
- Not washing hands
- Applying more than prescribed
- Applying to inconsistent areas daily
Why Application Site Matters in BHRT Cream Therapy
Topical hormone cream delivers medication through the skin, bypassing the digestive tract and avoiding initial first-pass liver metabolism.
After application, the hormone:
- Passes through the stratum corneum
- Moves into dermal microcirculation
- Enters systemic circulation
Absorption may vary depending on:
- Skin thickness
- Local blood flow
- Hydration level
- Age and hormonal status
- Underlying fatty tissue
Areas with thinner, well-perfused skin typically allow more consistent absorption of lipophilic hormones. Proper site selection supports consistent systemic exposure under prescriber guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions About BHRT and Hormone Cream
1. What is BHRT?
BHRT stands for bioidentical hormone replacement therapy, a prescriber-guided care approach using hormones structurally identical to those produced in the body.
2. Is BHRT the same as traditional hormone replacement therapy?
Both involve hormone therapy, but BHRT specifically refers to bioidentical hormones designed to match endogenous hormone structures.

3. What are the benefits of BHRT?
Potential benefits vary by individual and depend on clinical context. A licensed prescriber evaluates symptoms, laboratory findings, and medical history before determining whether bioidentical hormone replacement therapy is appropriate.
4. What are the risks of BHRT?
Hormone therapy carries potential risks and contraindications. Your healthcare provider assesses personal and family medical history before initiating care.
5. Where should I apply hormone cream?
Common areas include the inner forearms, inner thighs, outer thighs, and lower abdomen, as directed by your provider.
6. How much hormone cream should I apply?
Follow prescribed clicks; do not estimate manually.
7. Can I apply hormone cream to different body parts?
Yes, within the same recommended region; follow provider guidance.
8. When should I apply hormone cream?
Many clinicians recommend applying hormone cream at the same time each day to support consistent hormone levels. Follow your prescriber’s instructions regarding timing.
9. Should I rotate application sites?
Many clinicians recommend rotating within the same general region to minimize irritation.
10. How long does hormone cream take to absorb?
Creams typically absorb in about 2 minutes when applied properly to clean, dry skin.
11. Can hormone cream transfer to others?
Yes. Transfer is possible before the cream fully dries. Keeping the area covered and allowing complete absorption reduces this risk.
12. Can I shower after applying hormone cream?
Patients are often advised to wait approximately one hour before bathing or showering.

Why California Practitioners Choose ScriptWorks for Compounded BHRT
ScriptWorks supports prescribers managing bioidentical hormone replacement therapy through structured compounding processes and collaborative communication.
- PCAB-Accredited Standards
We are PCAB-accredited, reflecting adherence to recognized quality standards in non-sterile compounding. - Customized Bioidentical Hormone Formulations
We compound BHRT creams in concentrations tailored to each prescription. When clinically appropriate, combination formulations may include estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, or DHEA. - Precision Dispensing
Metered applicators such as Topi-Click support consistent dosing within personalized hormone therapy plans.
Clinical Collaboration
Our pharmacists collaborate with prescribers to discuss formulation details, base selection, and administration considerations.
ScriptWorks provides compounded hormone cream and BHRT services throughout California (shipping statewide), supporting prescribers and patients seeking customized hormone formulations and coordinated clinical care. Patients searching for bioidentical hormone therapy near them can contact our team to discuss prescription coordination and pharmacy collaboration.
If you’ve been prescribed compounded BHRT cream and have questions about application technique, metered dispensing, or hormone monitoring, our pharmacists are available to coordinate with your healthcare provider and support individualized hormone therapy management.
California prescribers exploring BHRT formulations and therapeutic considerations may contact our team for consultation. Our team is available to discuss compounding approaches, dispensing systems, and formulation parameters.
Related Prescriptions
References
- Davis, S. R., & Wahlin-Jacobsen, S. (2015). Testosterone in women—The clinical significance. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 3(12), 980–992. Link
- Cauley, J. A. (2015). Estrogen and bone health in men and women. Steroids, 99(Part A), 11–15. Link
- Stute, P., Neulen, J., & Wildt, L. (2016). The impact of micronized progesterone on the endometrium: A systematic review. Climacteric, 19(4), 316–328. Link
- Traish, A. M., Kang, H. P., Saad, F., & Guay, A. T. (2011). Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)—A precursor steroid or an active hormone in human physiology (CME). The Journal of Sexual Medicine, 8(11), 2960–2982. Link